Wireless Power Transfer For Electric Vehicle

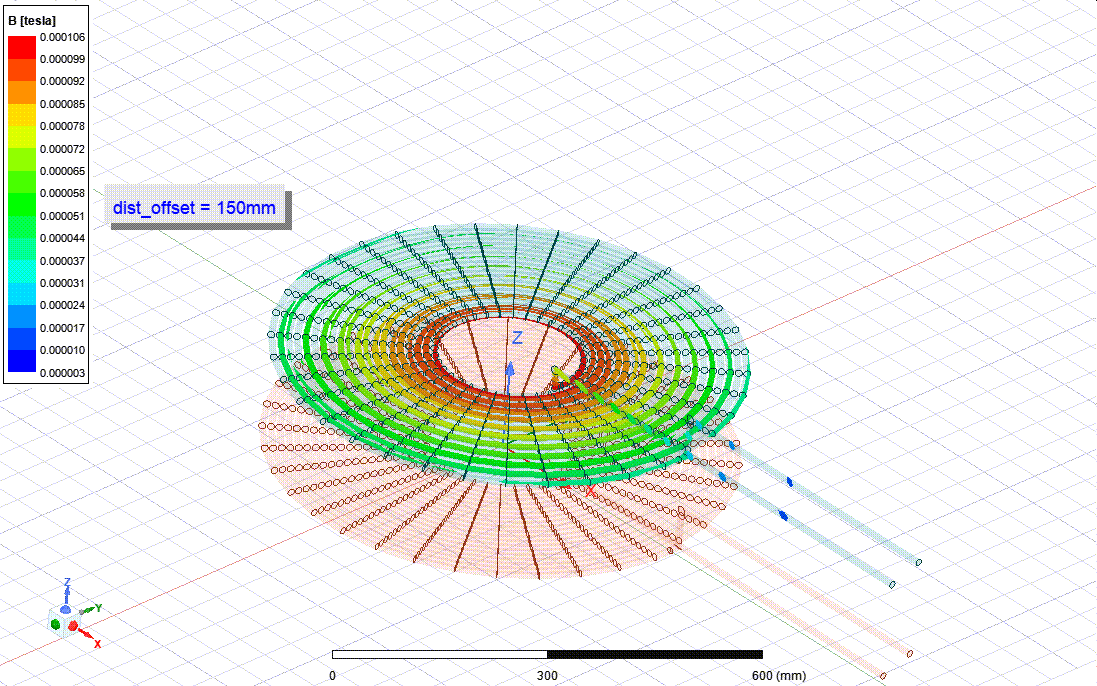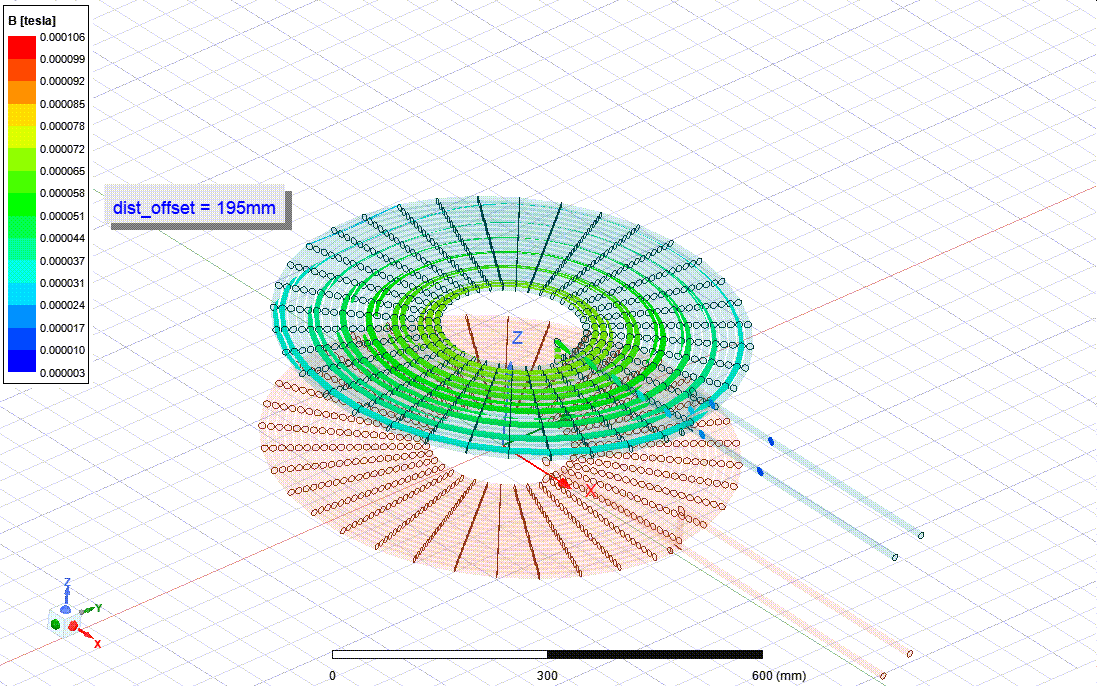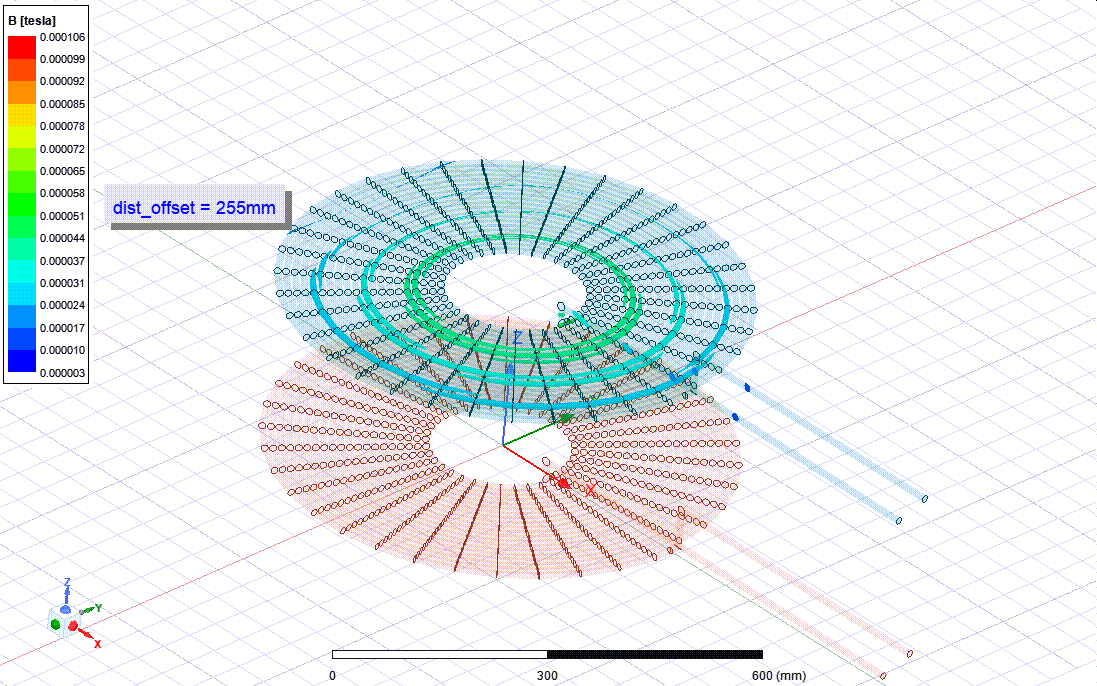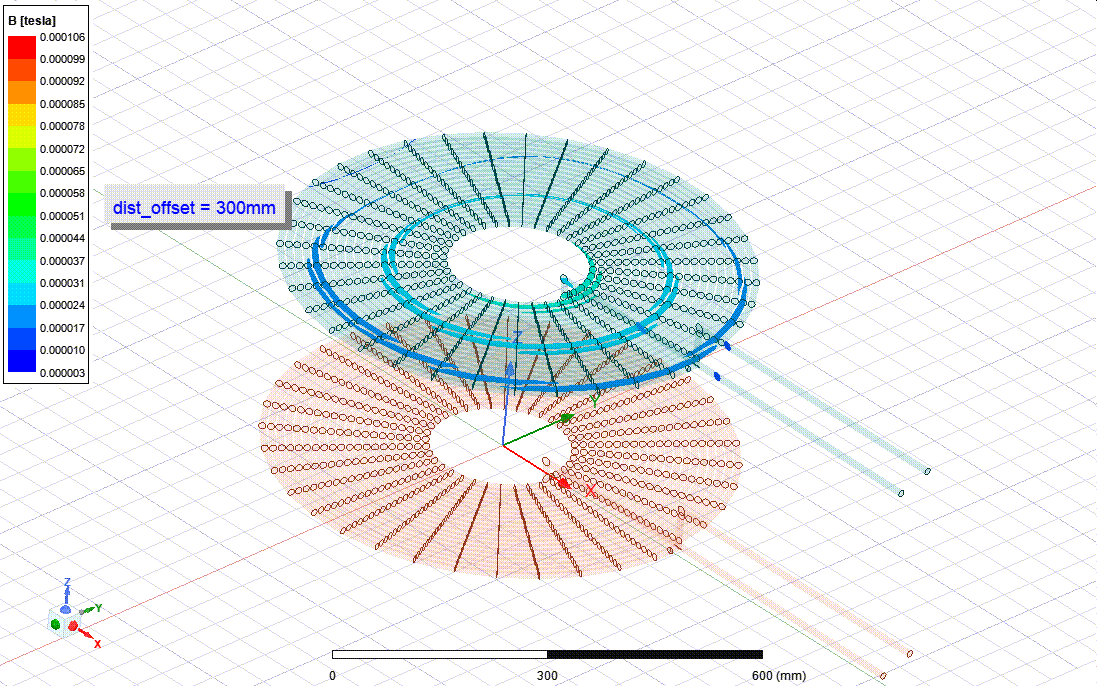
This works are the part of my undergraduate final year project - thesis. I am collaborating with three other members under the supervision of Dr. M Tanseer Ali, Assistant Professor, EEE, AIUB.
The goal is to design and Analysis a wireless power transfer system for electric vehicle considering SAE standard frequency level. For the finite element analysis Ansys Maxwell software and for the power electronics circuit Ansys Simplorer software are being used. A co-simulation between Maxwell and Simplorer is being used to calculate the full system parameters. Besides, I have a plan for a co-simulation between Maxwell and Mechanical to inspect the thermal properties and loss calculation.

The working principle of WPT is similar to the power transformer, but with some differences such as transformer have two coils placed very close to each other and usually each coil is wound on a ferrite material to increase the magnetic coupling but in case of WPT the core is the open air.
The basic elements to achieve WPT are two, transmitter and receiver.
The first one is to have a transmitter which requires circuits to convert the 50 Hz to the optimal WPT frequency to improve efficiency and reduce effects on human body, this frequency is below 10 MHz. This transmitter is connected to a coil which generates a changing magnetic field.
The second element is receiver, another coil to capture the magnetic field and EMF is generated between its terminals, also some circuits are required to change the frequency of the received power.
Finite Element Analysis Design

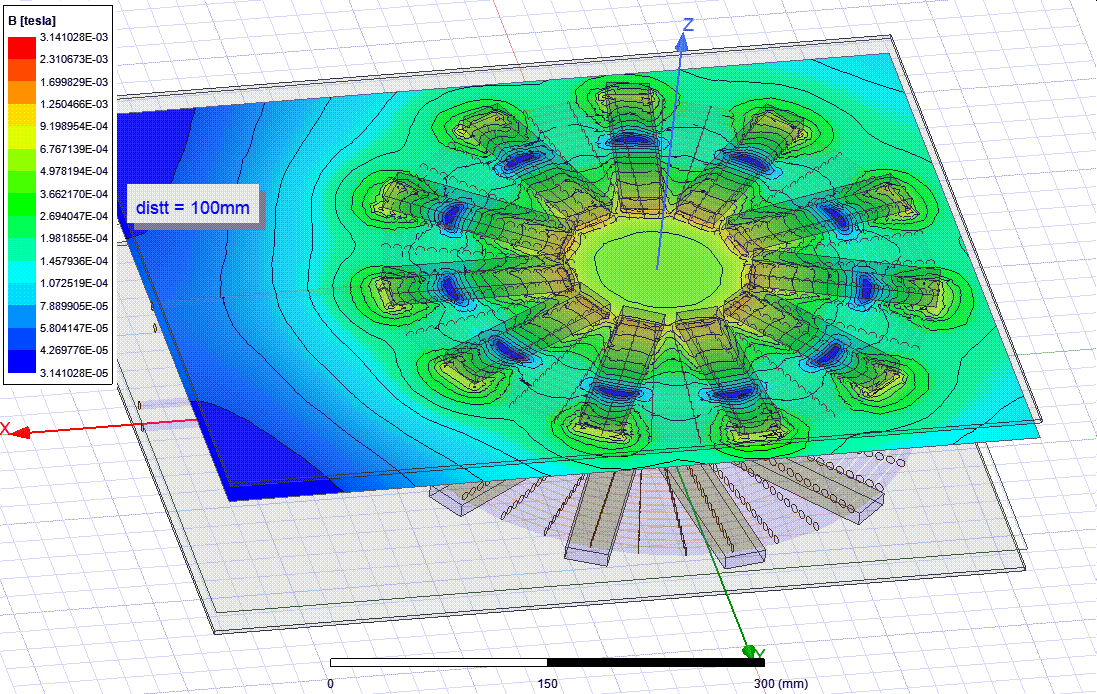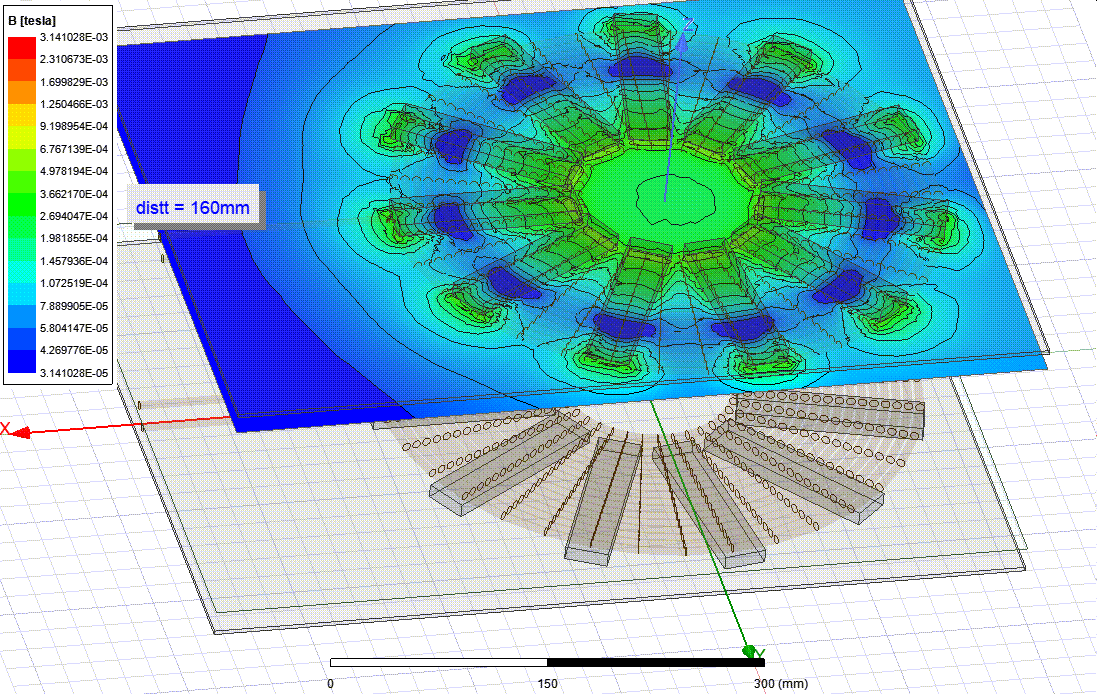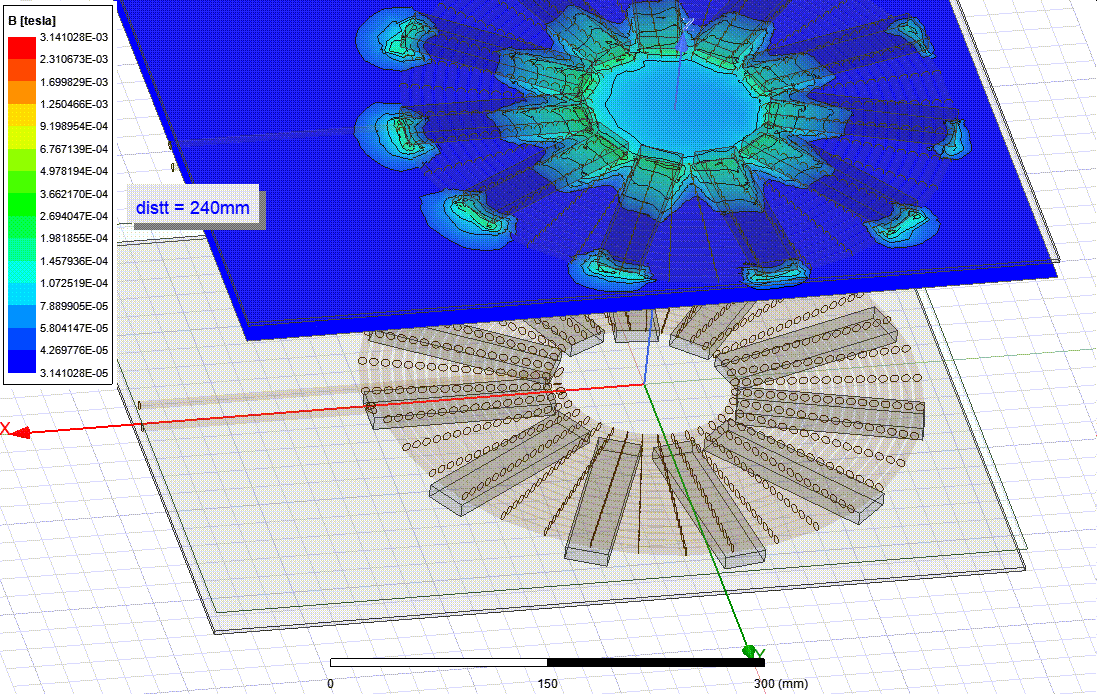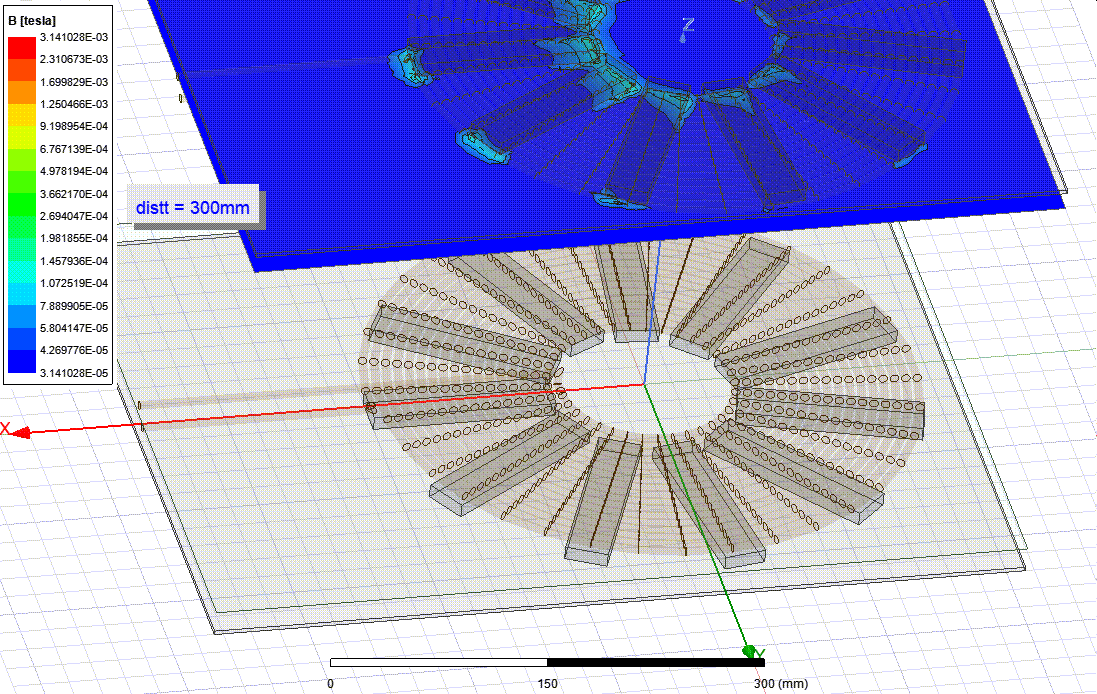

Ferrite Core Analysis



Pathfinder Designs


